Effects of Hydroxy Groups in Anthraquinone Dyes on Photocatalytic Activity of Visible-light-sensitized Pt-TiO2 for Hydrogen Evolution
F. Amano, Y. Akaki, A. Yamakata
Catalysis Surveys from Asia, in press, 2022
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10563-022-09370-y
https://rdcu.be/cXZehf (full-text access to a view-only version)
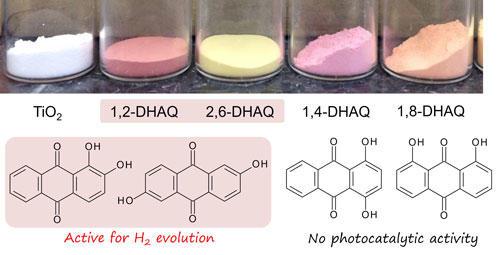
Alizarin (1,2-dihydroxyanthraquinone) is a stable red photoredox sensitizer. We explored the effect of the hydroxy substituents of 9,10-anthraquinone (AQ) molecules on the photocatalytic hydrogen evolution over a dye-sensitized Pt-TiO2 system under visible-light irradiation. The 2-hydroxy group in AQ dyes was necessary to induce photocatalytic H2 evolution. By contrast, the 1-hydroxy group was the anchoring group to increase the adsorption amount of the dyes on the TiO2 surface. Using time-resolved infrared spectroscopy, we found that the 2-hydroxy group suppresses the back electron transfer from TiO2 particles to the dye.